-
07-13 2025
What Is Ammonium Heptamolybdate?
As a typical molybdate, ammonium heptamolybdate is also called ammonium paramolybdate. It is a colorless to light green crystalline powder composed of transition metal molybdenum, non-metallic oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen. It is an ammonium molybdate composed of ammonium ions and heptamolybdate ions. Its name can be divided into Ammonium heptamolybdate or Ammonium paramolybdate. Its chemical formula is (NH4)6Mo7O24, its molar mass is 1163.9g/mol, and its CAS registration number is 12027-67-7 or 12054-85-2 (tetrahydrate).
-
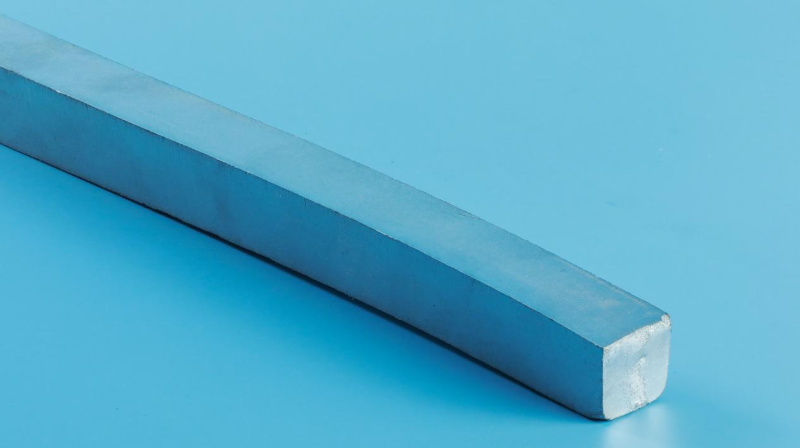
07-13 2025
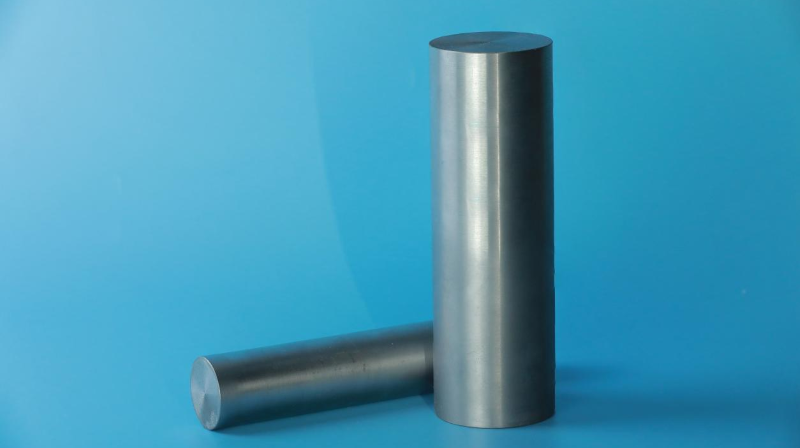
What Is Molybdenum Bar?
As a representative product of refractory metal molybdenum, molybdenum bar is a rod-shaped product with high-purity molybdenum as the main material. It is often called molybdenum rod or molybdenum rod in the industrial field. The purity of molybdenum bar is as high as 99.7%. Due to its thermal, mechanical, chemical and electrical properties, it has become the core basic material of many industries such as smelting and power equipment.
-
07-13 2025
What Is the Principle of Molybdenum Metal Bar in the Manufacture of Vacuum Devices?
The principle of molybdenum metal bar in the manufacture of vacuum devices is mainly based on the unique physical and chemical properties of molybdenum matching the working requirements of vacuum devices. The following is an analysis from the material properties, device working environment and specific application principles: I. The core physical and chemical properties of molybdenum metal bar and the adaptability of vacuum devices:
-
07-13 2025
Must-Read! Roasted Molybdenum Concentrates Industry Information
Roasted molybdenum concentrates, also known as molybdenum trioxide or industrial molybdenum oxide, generally refers to roasted sand after molybdenum concentrate is roasted. Molybdenum concentrate is usually oxidized and roasted at 630℃~700℃ to convert molybdenum sulfide into industrial molybdenum trioxide, which is the raw material for producing ferromolybdenum and ammonium molybdate. In recent years, China has produced about 200,000 tons of roasted molybdenum concentrates each year, with a value of about 36 billion yuan, of which about 30% is used to produce ammonium molybdate, and then to produce molybdenum chemicals and molybdenum metal products, and the rest is used to process ferromolybdenum raw materials. Roasted molybdenum concentrates are divided into ordinary and high-soluble. In addition, according to the latest national standard classification, it is more refined. In addition to the above two categories, there are also blocks. We will not introduce it in detail here. Today we will mainly talk about the two types of ordinary and high-soluble in detail.